Hemorrhoids( Piles ) Introduction 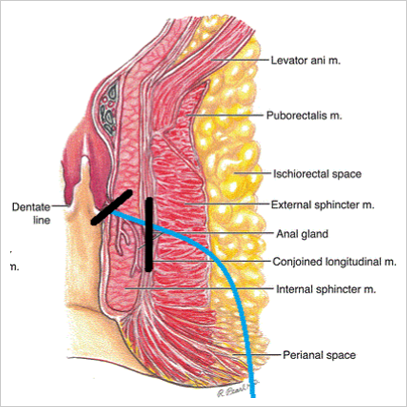
What are Hemorrhoids?
- Hemorrhoids are vascular structures in the anal canal. In their normal state, they are cushions that help with stool control. They become pathological when swollen or inflamed. At this point they are treated as hemorrhoidal disease
- Huge problem for society. Symptomatic hemorrhoids are thought to affect at least 50% of the US population at some time during their lives, and around 5% of the population is affected at any given time
Common Causes Of Hemorrhoids 
- Straining
- Constipation
- Ageing
- Trauma
- Lack of fiber rich diet
Other Causes 
- Local anorectal deformities
- Ascites
- Pregnancy
- Portal hypertension
- Neurological diseases like paraplegia
Generally, hemorrhoids can be divided into two types:
Internal hemorrhoid and External hemorrhoid.
External hemorrhoid usually requires no specific treatment unless it becomes acutely thrombosed or causes patients discomfort. Meanwhile, low-graded internal hemorrhoids can be effectively treated with medication and non-operative measures (such as rubber band ligation and injection sclerotherapy). Surgery is indicated for high-graded internal hemorrhoids, or when non-operative approaches have failed, or complications have occurred. Although excisional hemorrhoidectomy remains the mainstay operation for advanced hemorrhoids and complicated hemorrhoids, several minimally invasive operations (including Ligasure hemorrhoidectomy, doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation and stapled hemorrhoidopexy) have been introduced into surgical practices in order to avoid post-hemorrhiodectomy pain. This article deals with some fundamental knowledge and current treatment of hemorrhoids in a view of a coloproctologist - which includes the management of hemorrhoids in complicated situations such as hemorrhoids in pregnancy, hemorrhoids in immunocompromised patients, hemorrhoids in patients with cirrhosis or portal hypertension, hemorrhoids in patients having antithrombotic agents, and acutely thrombosed or strangulated hemorrhoids.
How you come to know you have hemorrhoids/ Piles ? 
Hemorrhoids are the most common cause of rectal and anal complaints. The most common complaint symptoms are:
- painless bleeding,
- anal itching,
- pain,
- swelling and feeling a lump at the anus are all associated with an inflamed hemorrhoid.
- Tissue bulging around the anus
- Leakage of feces or difficulty cleaning after a bowel movement
Treatment of Haemorrhoids
Non Interventional Treatment of Hemorrhoids
To diagnose hemorrhoids, At Karan Hospital our doctors will examine your rectum and anus, and may insert a gloved finger into the rectum. If there is bleeding, testing should include a procedure that allows your healthcare provider to look inside the anus (called anoscopy) or colon (sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy). (See patient guide link".)
If you have rectal bleeding you should consult our doctor. You need to make sure bleeding is not from a more serious condition such as colorectal or anal cancer. Treatment may include warm baths and a cream or other medicine. If you have large hemorrhoids, you may need surgery and other treatments.
Treatment Indicated only in 1st degree
- Banding
- Infrared coagulation (IRC)
- Sclerotherapy
- Cryotherapy
Minimal Invasive Procedures ( Without any Cutting )
- Laser ( Laser Haemorrhoidoplasty )
- Doppler Guided HAL (Hemorrhoidal artery Ligation) with RAR
IRC 
The IRC is the most widely used office instrument for the treatment of hemorrhoids – in the world.
Indications for Infrared Coagulation
Bleeding, mucoid discharge and pruritus are symptoms usually treated easily by coagulation. All internal hemorrhoids can benefit substantially from IRC treatment, especially Grade I.
Advantages
- No Hospital stay
- No Anaesthesia
- No Pain
- No Blood loss
- Immediate return to routine work
- Success rate 95% effective
LASER Treatment of Haemorrhoids / Piles
What is Laser ?
LightAmplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Laser Light is transformed into thermal energy which leads to cutting, ablation, vaporization, hemostasis and coagulation of tissue
What do Patients Expect from a Surgeon?
- Minimal Invasive Procedure
- Minimal Post-operative Pain
- Short Hospital Stay
- No Post-operative Dressings
- Faster Return to Work
Principle of Laser in Haemorrhoids
- Dearterialisation - Reduces blood supply to anal cushions
- Shrinkage - When coagulation occurs
- Fibrosis - Which would shrink and fix the prolapsing element in long term.
Advantages of Laser for Haemorrhoids
- Minimal Pain
- Least risk of Complications
- Least Tissue Trauma
- Absolutely blood less
- Short Hospital Stay
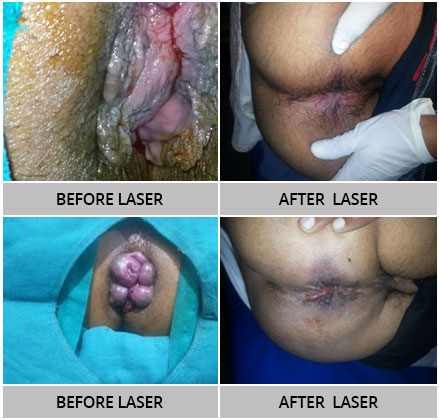
Laser Surgery Results – Before and After Surgery
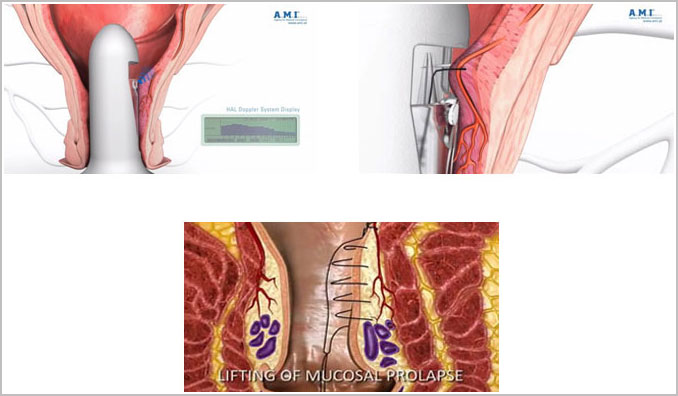
Doppler Guided HAL (Hemorrhoid artery Ligation) with RAR for management of Piles
The DG-HAL & RAR is a safe and less painful procedure and it makes patients return to work more quickly. Also, the DG-HAL & RAR procedure can correct symptomatic, prolapsed (Grade II~IV) hemorrhoids with satisfactory results, which is difficult with DG-HAL alone. Therefore, the DG-HAL & RAR is an effective alternative for the treatment of symptomatic, prolapsed (Grade II~IV) hemorrhoids. Doppler-guided hemorrhoid artery ligation is a minimally invasive technique for the treatment of symptomatic hemorrhoids that has been applied successfully for grade II and III hemorrhoids.
Advantages of HAL / RAR
- Less pain
- Less analgesics
- Shorter hospital stay
- Faster return to work











